Computer Networks 🖥️
Welcome to the captivating world of computer networks! Have you ever wondered how information magically travels from one device to another? Or how we can connect with people around the world within seconds? In this chapter, we will embark on an exciting journey to uncover the secrets of computer networks and understand why they are so vital in our daily lives. Get ready to dive into a realm of connections, communication, and endless possibilities!
Chapter 1: The World of Computer Networks
What is a Computer Network?
Imagine you have a group of friends who all love to play games. Sometimes you gather in the same room and play together, but other times you're in different rooms and want to play together too. To make this happen, you connect your devices through a network. A computer network is like a magical web of connections that allows computers, smartphones, and other devices to talk to each other, share information, and work together.
What is a computer network?
Why are Computer Networks Important?
Computer networks have become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing the way we live, work, and play. Let's explore some real-world examples to understand their significance:
Communication: Networks help us connect with our friends and family, no matter where they are in the world. We can send messages, make video calls, and share memories instantly.
Sharing Information: Networks allow us to access vast amounts of information. Have you ever searched for something on the internet, read an e-book, or watched an educational video? All of this is possible because of computer networks.
Online Entertainment: Networks bring us joy and entertainment. Streaming services like Netflix and YouTube rely on networks to deliver our favorite movies, shows, and videos directly to our screens.
Business and Economy: Networks are the backbone of modern businesses. They enable companies to communicate with clients, share data, and conduct online transactions. They have opened up new opportunities for entrepreneurs and global commerce.
Which of the following is NOT an example of why computer networks are important?
How do Computer Networks Impact Our Daily Lives?
Computer networks have become an essential part of our daily routines, often without us even realizing it. Let's explore some ways networks impact our lives:
Social Connections: Networks help us connect with friends through social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat. We can share photos, experiences, and stay updated on each other's lives.
Online Learning: Networks provide us with access to educational resources and online courses. We can learn new skills, explore different subjects, and expand our knowledge.
Online Gaming: Networks allow us to play games with friends and people from around the world. Whether it's building virtual worlds together or competing in thrilling races, networks make it possible.
Remote Work: Networks enable many people to work from home or any location with an internet connection. We can collaborate with colleagues, attend online meetings, and accomplish tasks without being physically present.
How do computer networks impact our daily lives?
Chapter 2: Exploring Different Types of Networks
In this chapter, we will embark on an adventure to explore the fascinating realm of different types of networks. We will discover two important types: Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs). Get ready to unravel the secrets behind their applications, explore real-world examples, and understand the differences between them. Let's dive in!
Local Area Networks (LAN)
Imagine you are in your own neighbourhood, where you can easily connect with your friends who live nearby. Similarly, a Local Area Network, or LAN, is a network that connects devices in a small area, like a home, school, or office. LANs are like a close-knit community, where devices can communicate and share information easily.
Real-World Examples:
Home Network: Have you ever connected your computer, smartphone, and game console to the same Wi-Fi network at home? That's a LAN! It allows devices in your home to share resources like printers, files, and an internet connection.
School Network: Schools often have LANs that connect computers in computer labs, classrooms, and libraries. This enables students and teachers to share educational resources and collaborate on projects.
What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
Wide Area Networks (WAN)
Now, let's expand our horizons and venture beyond our local neighborhoods. A Wide Area Network, or WAN, connects devices over a larger geographical area, often spanning cities, countries, or even continents. WANs are like long highways that allow devices to communicate across vast distances.
WANs connect devices using various technologies, including telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, and satellite links. These technologies enable the transmission of data over long distances, making it possible for devices in different locations to communicate with each other.
Real-World Examples:
Internet: The internet itself is a massive WAN that connects devices worldwide. It enables people from different parts of the world to communicate, share information, and access online resources.
Mobile Networks: When you use your smartphone to make a call, send a text, or browse the internet, you are using a WAN provided by your mobile network carrier. It connects your device to the network towers and allows communication over long distances.
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
Differences between LANs and WANs
Although both LANs and WANs are networks, they differ in various aspects. Let's explore the differences between them:
Size: LANs cover a small area, typically within a building or a campus, while WANs span larger geographical areas, often connecting devices across cities, countries, or continents.
Distance: LANs have shorter distances between connected devices, making communication faster and more reliable. In contrast, WANs cover long distances, and data transmission may take longer due to the physical limitations of signal travel.
Speed: LANs generally provide faster and more reliable connections compared to WANs. Since LANs cover smaller areas, data transmission within the network is swift and efficient. WANs, on the other hand, may experience latency and slower speeds due to the longer distances involved.
Whether it's collaborating with classmates in a LAN or accessing information globally through a WAN, these network types have transformed the way we communicate, share information, and conduct business.
What is one difference between LANs and WANs?
Chapter 3: Meet the Network Superstars
In this chapter, we will be introduced to some important network superstars: routers, switches, and modems. Just like superheroes with unique abilities, these devices play crucial roles in the operation and management of computer networks. Get ready to embark on an exciting journey as we unravel the mysteries of these network superstars and understand their functions.
Routers - The Traffic Directors
Imagine you are in a bustling city with multiple roads leading to different destinations. How do you know which road to take to reach your desired location? That's where a router comes in. A router is like a traffic director for data packets in a computer network. It determines the most efficient path for data to travel from one device to another.
Alternatively, think of a router as a post office sorting facility. When you send a letter, it gets picked up from your mailbox and brought to the local post office. From there, it goes through a sorting process, where the post office staff determines the most efficient route for your letter to reach its destination. The letter is then forwarded to the appropriate post office nearest to the recipient's address. Similarly, routers examine the destination address of data packets and forward them to the correct network or device.
The function of Routers
Path Determination: Routers determine the best path for data packets to reach their destinations based on factors like network congestion, speed, and reliability. They use routing protocols and algorithms to make these decisions.
Network Segmentation: Routers can divide a network into smaller subnetworks, called subnets. This segmentation helps manage network traffic and improves network performance and security.
Internet Gateway: Routers act as gateways between LANs and the internet. They provide a connection point for devices in a local network to access resources and services on the internet.
What is the role of routers in a computer network?
Switches - The Network Traffic Managers
Now that we understand the role of routers in directing data traffic between networks, let's meet the network traffic managers - switches. Switches are like traffic managers at an intersection, ensuring smooth and efficient communication within a network.
Switches are responsible for connecting devices within the same network, such as a LAN. They receive data packets from one device and determine the appropriate device to send them to. Switches are essential for local network communication, enabling devices to exchange information seamlessly.
Imagine you are in a classroom where students need to communicate with each other. The teacher acts as a switch, ensuring that messages from one student reach the intended recipient. When a student raises their hand and asks a question, the teacher listens, identifies the student the question is directed to, and allows them to respond. Switches in a network perform a similar function, directing data packets to the correct destination device within a LAN.
Function of Switches
Packet Forwarding: Switches receive data packets and determine the appropriate destination device based on the Media Access Control (MAC) addresses of the devices connected to the switch. They forward the data packets directly to the intended recipient, reducing network congestion and improving performance.
Broadcast Management: Switches prevent unnecessary flooding of data packets by delivering them only to the device they are intended for. This helps optimize network bandwidth and ensures that network resources are used efficiently.
Port Management: Switches have multiple ports to connect devices. They manage the flow of data packets across these ports, ensuring that each packet reaches its intended recipient.
What is the role of switches in a computer network?
How do switches and routers differ?
The differences between switches and routers are illustrated in this diagram from cable-solutions.com:
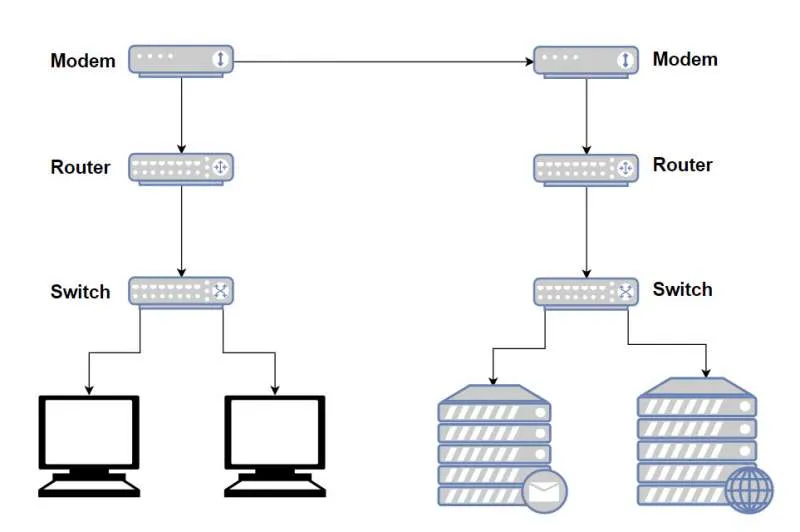
A switch connects devices within the same network, while a router forwards data packets between different networks.
Chapter 4: The Secret Codes of the Internet
Get ready to dive into the realm of IP addresses, understand how they help identify devices on a network, and participate in fun activities to practice identifying and understanding these codes.
What are IP Addresses?
Imagine you are at a party, and you want to invite your friends over to your house for a sleepover. To do so, you need to provide them with your home address so they can find their way. Similarly, in the world of computer networks, IP addresses act as unique identifiers for devices connected to a network.
An IP address is like a digital home address for devices on a network. Just like every house has its own unique address, every device connected to a network has its own unique IP address. This address helps devices communicate with each other, ensuring that data packets are sent to the correct destination.
There are two main types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4: IPv4 addresses are the most common type of IP address used today. They consist of four sets of numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by periods. For example, 192.168.0.1.
However, IPv4 addresses have a limited number of unique combinations, which is why the world is gradually transitioning to IPv6.
IPv6: IPv6 addresses are the future of IP addressing. They are designed to provide a much larger pool of unique addresses to accommodate the growing number of devices connected to the internet. IPv6 addresses are represented by eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons. For example, 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
What is an IP address?
Role of IP Addresses
Device Identification: IP addresses uniquely identify each device connected to a network. When you send a message or request data from a website, your device's IP address is included in the data packets. This allows the recipient to know where to send the response.
Routing Data: Just as mail carriers use addresses to deliver letters, routers use IP addresses to route data packets across networks. When you send data to a website, routers examine the IP address of the destination and determine the best path to deliver the data.
Network Security: IP addresses play a crucial role in network security. They help identify the source and destination of data packets, enabling network administrators to monitor and control network traffic, detect potential threats, and implement security measures.
What is the primary function of IP addresses in a computer network
A fun activity!
Now it's time to put your IP address skills to the test with a fun activity!
Imagine you are a scientist in a virtual world and need to create IP addresses for various objects. Assign unique IP addresses to your virtual pets, houses, and vehicles. When you call your friend, refer to them by their IP address name!
Conclusion
Congratulation on completing this exciting journey through the world of computer networking and cybersecurity! Throughout this course, we have explored various concepts, from understanding the basics of computer networks to unravelling the secret codes of the internet. Let's recap what we've learned and celebrate your newfound knowledge and skills.
Chapter 1: The World of Computer Networks: In this chapter, we discovered the wonders of computer networks and their importance in our daily lives. We learned how networks connect devices, enabling us to communicate, share information, and access the vast resources of the internet. From chatting with friends to streaming videos and playing online games, computer networks are the backbone of our digital world.
Chapter 2: Exploring Different Types of Networks: In this chapter, we dived deeper into the world of networks, exploring the differences between Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs). We discovered real-world examples of LANs, such as school networks, and WANs, like the internet itself. Understanding these networks helped us appreciate their applications and the impact they have on our lives.
Chapter 3: Meet the Network Superstars: In this chapter, we were introduced to the network superstars: routers and switches. We learned about their roles in a computer network, with routers directing data packets and switches connecting devices.
Chapter 4: The Secret Codes of the Internet: In our final chapter, we uncovered the secret codes of the Internet, known as IP addresses. We learned that IP addresses are like digital addresses for devices on a network, allowing data packets to be sent to the correct destination.
Throughout this course, we emphasized the importance of staying safe and secure in the digital world. We discussed the significance of protecting personal information, avoiding online scams, and being responsible digital citizens. Remember, with great power comes great responsibility!